
Yoga for mindfulness
YOGA BASICS
Yoga poses, known as 'asanas,' began as a very short list. Today, there are thousands of yoga poses, and more and more are being added to the list. While yoga poses cannot be definitively grouped into categories, here we will look at common poses based on the six parts of the most basic yoga sequence.
-
Grounding
-
Warm Up
-
Sun and Moon Salutations
-
Standing and Balancing
-
Floor Work
-
Seated and Supine
-
Prone and Inversions
-
-
Savasana
Grounding:
At the beginning of your practice, it is important to take 5-10 minutes for grounding. What does this mean? To come to the present moment, letting go of the past and the future, and focusing on your breath. At this time, you may also wish to set an intention for the practice. Grounding can be done in a variety of positions, but the most common is Sukhasana (Easy Pose).

Poses from Tummee.com
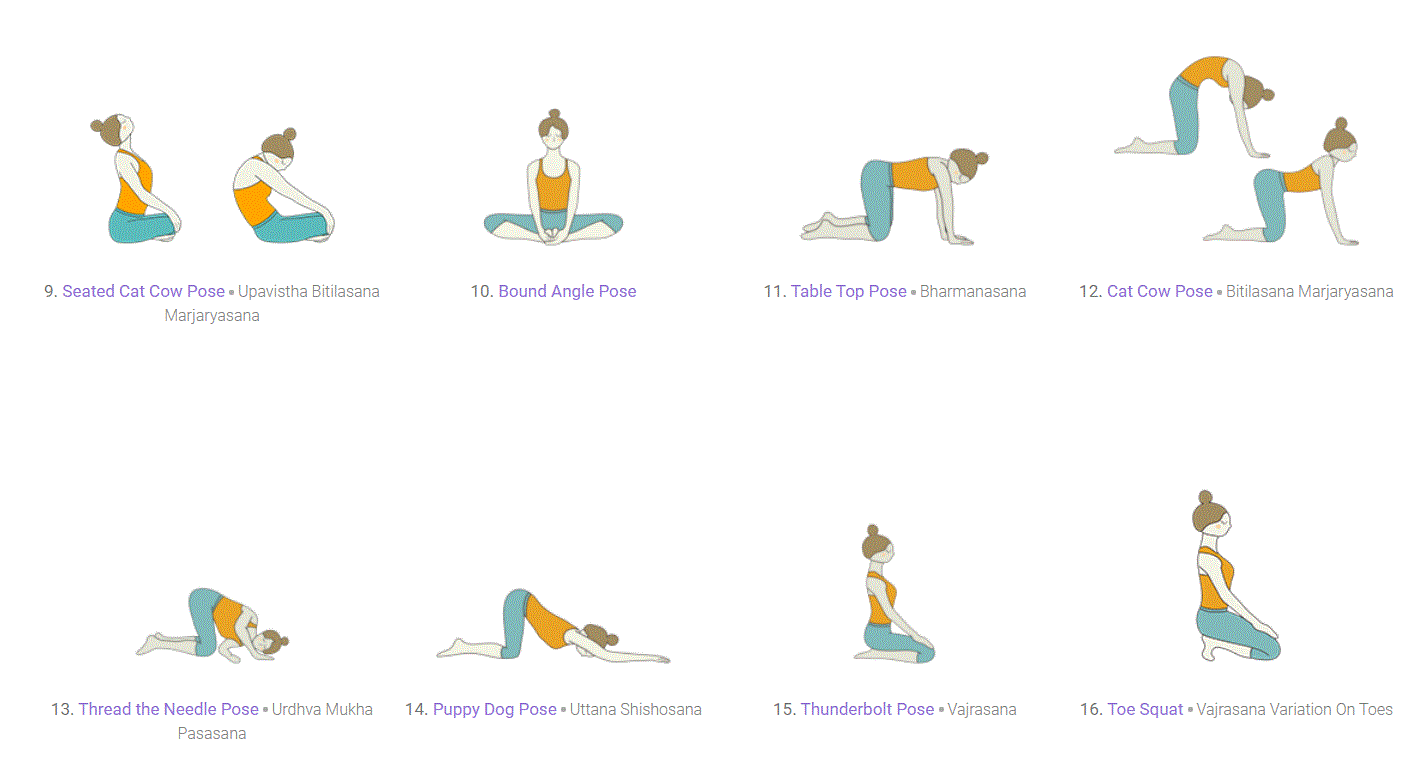
Warm Up:
In the warm up, we begin to connect our breath with movement. Warm up can be quite gentle or jump into more active movement, and can be done completely on the floor, standing, or a mix of both. Most important is to move your spine in all directions, bending forward and extending back, reaching side to side and twisting, in order to prepare the body for further poses. Below are some ideas to include in a warm up:

Sun or Moon Salutations:
As part of warm up, Sun Salutations can be used to create heat in the body by completing just a few rounds or the suggested 12 rounds, and they can be done at a gentle to vigorous pace. As the name suggests, Sun Salutations are traditionally done at sunrise while facing the direction of the sun, but it is definitely not required. Moon Salutations are a calming and quieting flow great for low energy days.
Poses from Tummee.com

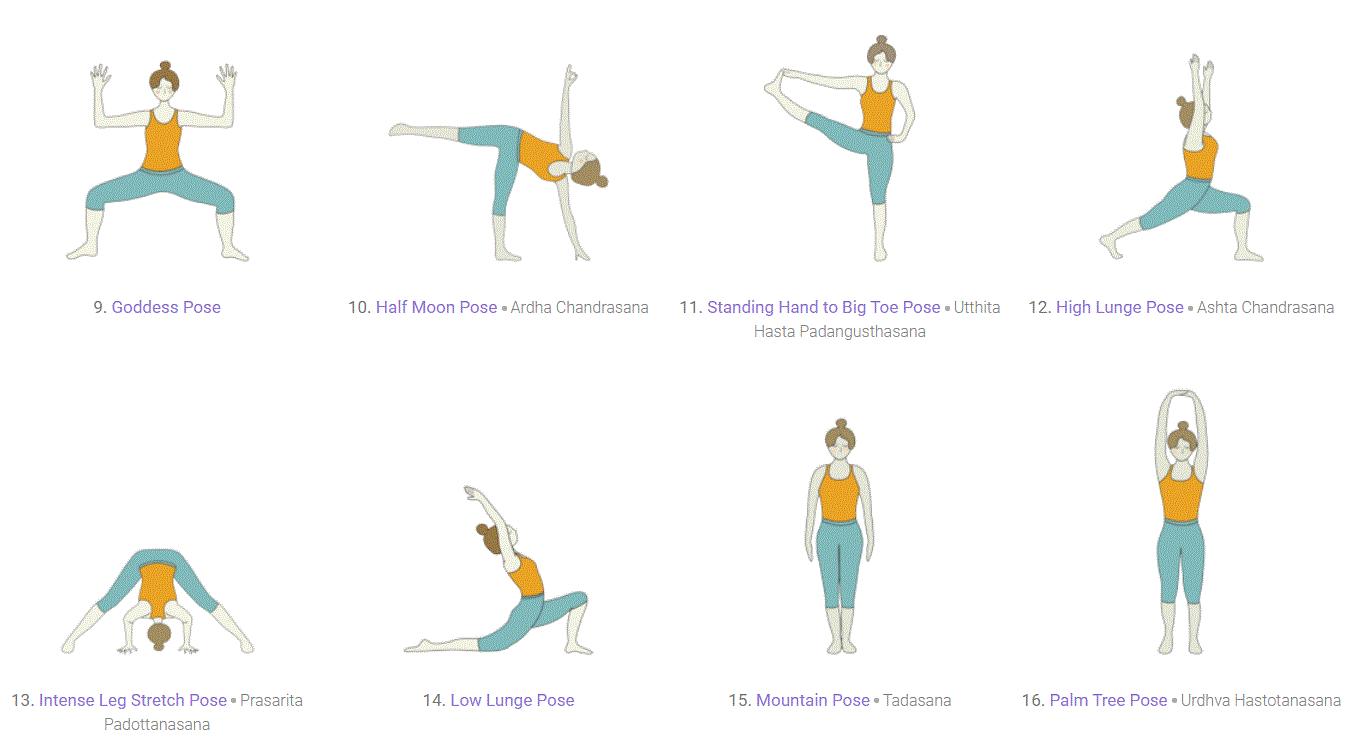
Standing or Balancing:
The benefits of poses in the standing or balancing part of a sequence include strengthening and stretching both the lower and upper body muscle groups, but, obviously, improvement in balance is one of the main benefits. These poses also increase awareness of alignment, thus developing kinesthetic intelligence. Below are some of the most common standing poses.
Poses from Tummee.com


Poses from Tummee.com
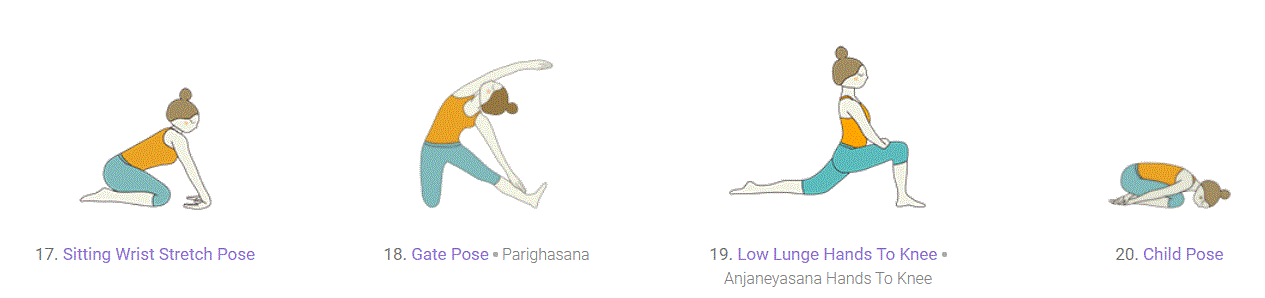
Floor Work - Seated and Supine:
Whether seated or supine (lying face upward), yoga poses on the floor are ideal for working on flexibility and can also provide opportunity for yoga practice to those with less mobility or injury. However, after having created some heat in standing poses, seated or supine poses provide great opportunity to deepen your practice while preparing for savasana.
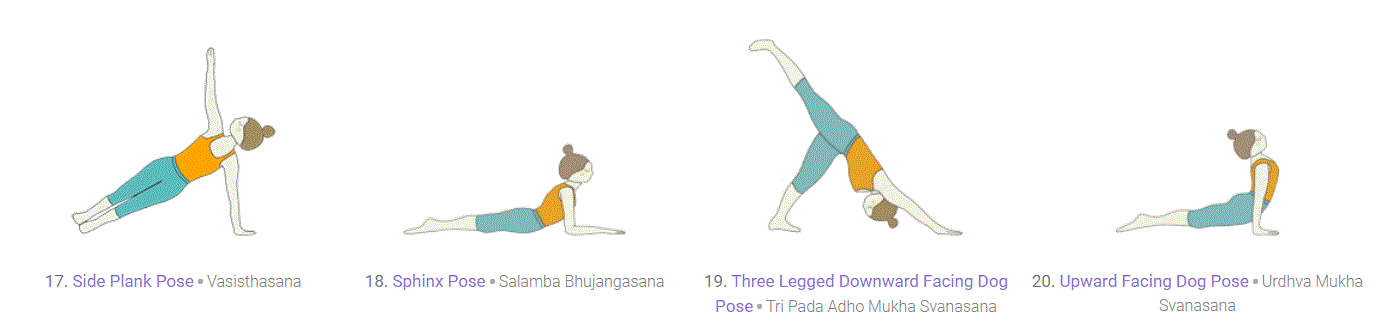
Floor Work - Prone and Inversion:
Prone poses are completed when facing towards the floor, either with the belly against the floor or lifted, and inversion poses involve the heart being higher from the ground than the head. While handstand or headstand often come to mind first when considering inversions, there are also many gentle options such as downward facing dog, supported shoulder stand or even standing forward fold.



Poses from Tummee.com
Savasana:
After taking poses to stretch, strengthen, open and release tension in the muscles, the final pose is savasana or corpse pose. While often looked forward to, this pose is considered by many to be the most challenging pose in yoga. It is not meant for mental planning or sleep, but rather an intentional relaxation of both the body and mind, absorbing the work of the practice, calming the mind, and reducing stress and fatigue.


Poses from Tummee.com
Poses from Tummee.com
Yin Yoga Asanas:




Poses from Tummee.com

POSES / ASANAS
















